Not All Shoppers Are Equal
Identifying High-Growth and High-Risk Customer Segments
Overview:
The purpose of this analysis is to identify distinct customer segments using clustering techniques (e.g., K-Means) to enable more targeted marketing, improved customer engagement, and optimized resource allocation. By understanding the characteristics and behaviors of each segment, the company aims to refine its marketing efforts, tailor loyalty programs, and reduce churn.
Key Results:
-
Number of Customer Segments:
The analysis reveals 3 meaningful customer segments identified through clustering. The "elbow" point at k = 3 suggests that three segments provide the most meaningful and actionable segmentation, balancing accuracy and simplicity. -
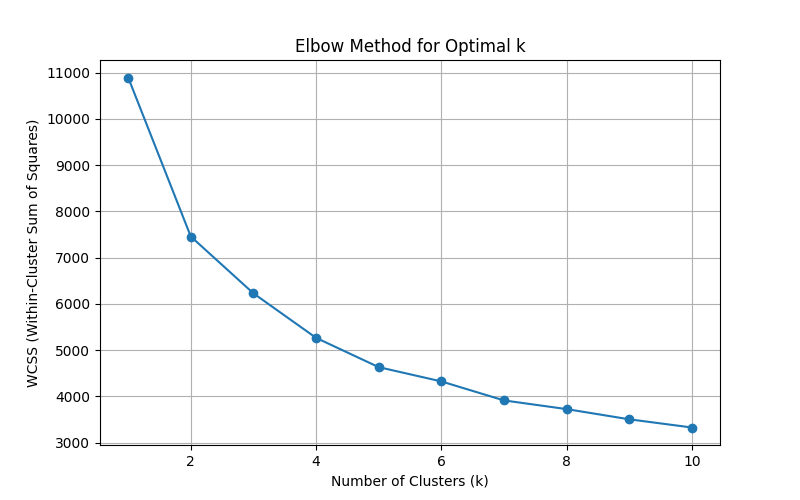
-
Segment Characteristics:
-
Cluster 0 (Silent High-Value):
- High Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) but low engagement and spending scores.
- Likely represents infrequent but high-value customers, possibly acquired through large transactions but not consistently engaged.
-
Cluster 1 (Low-Value Inactives):
- Very low scores across all metrics (CLV, engagement, spending score, frequency).
- This segment represents low-value, low-engagement customers, possibly at risk of churn or contributing little to revenue.
-
Cluster 2 (Loyal High Spenders):
- High engagement, moderate-to-high CLV, high spending score, and frequent purchases.
- Represents loyal, consistent spenders with high potential for retention and upsell opportunities.
-
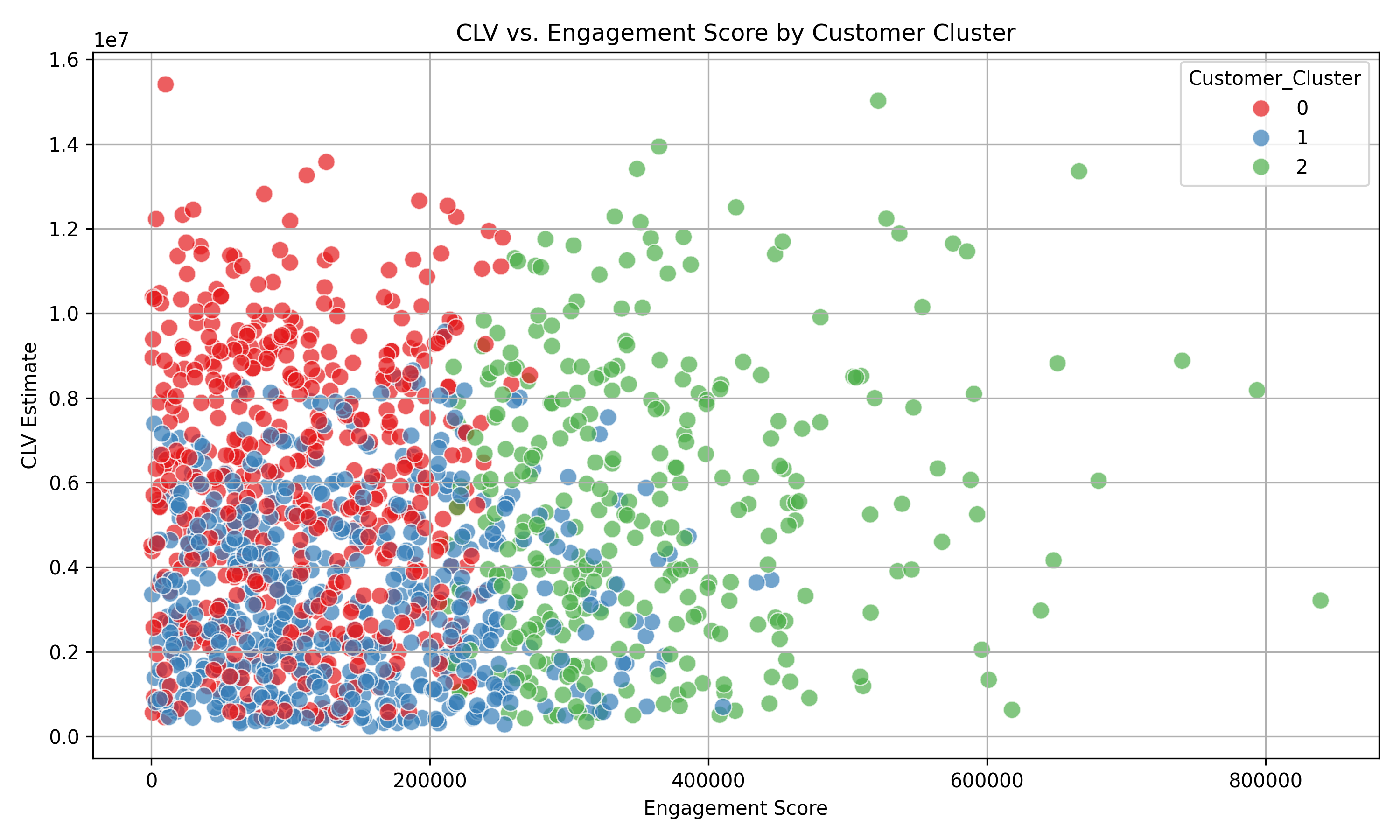
-
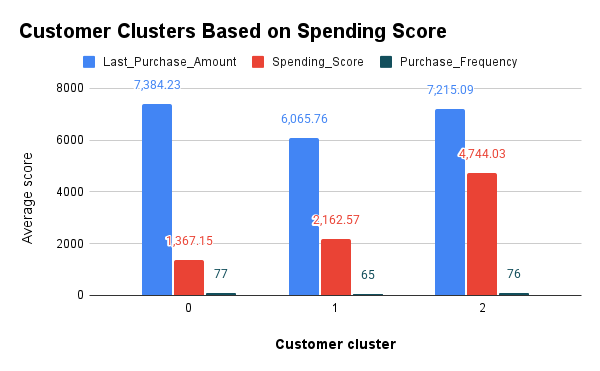
-
Cluster 0 (Silent High-Value):
-
High-Value or High-Potential Segments:
Cluster 2 stands out as the high-potential segment due to its high engagement, spending score, and frequency of purchases. This segment is ideal for focused loyalty programs, upsell strategies, and maximizing customer lifetime value. -
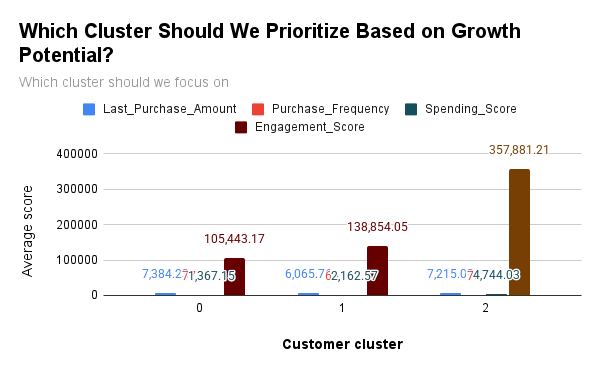
-
Risk of Churn or Inactivity:
Cluster 1 is at the highest risk of churn, with low purchase frequency and moderate engagement. These customers are long-term but show declining activity. Targeting this segment for reactivation or personalized offers could reduce churn. -
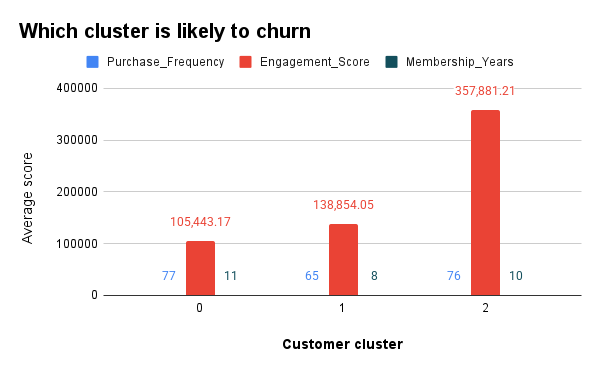
-
Stability and Actionability Over Time:
- Customer CLV increases steadily with membership duration, suggesting that retaining customers over time significantly increases their value to the business.
- Purchase frequency remains relatively stable across membership years, indicating that customers' spending amount (or basket size) may increase, but their frequency of purchases does not.
-
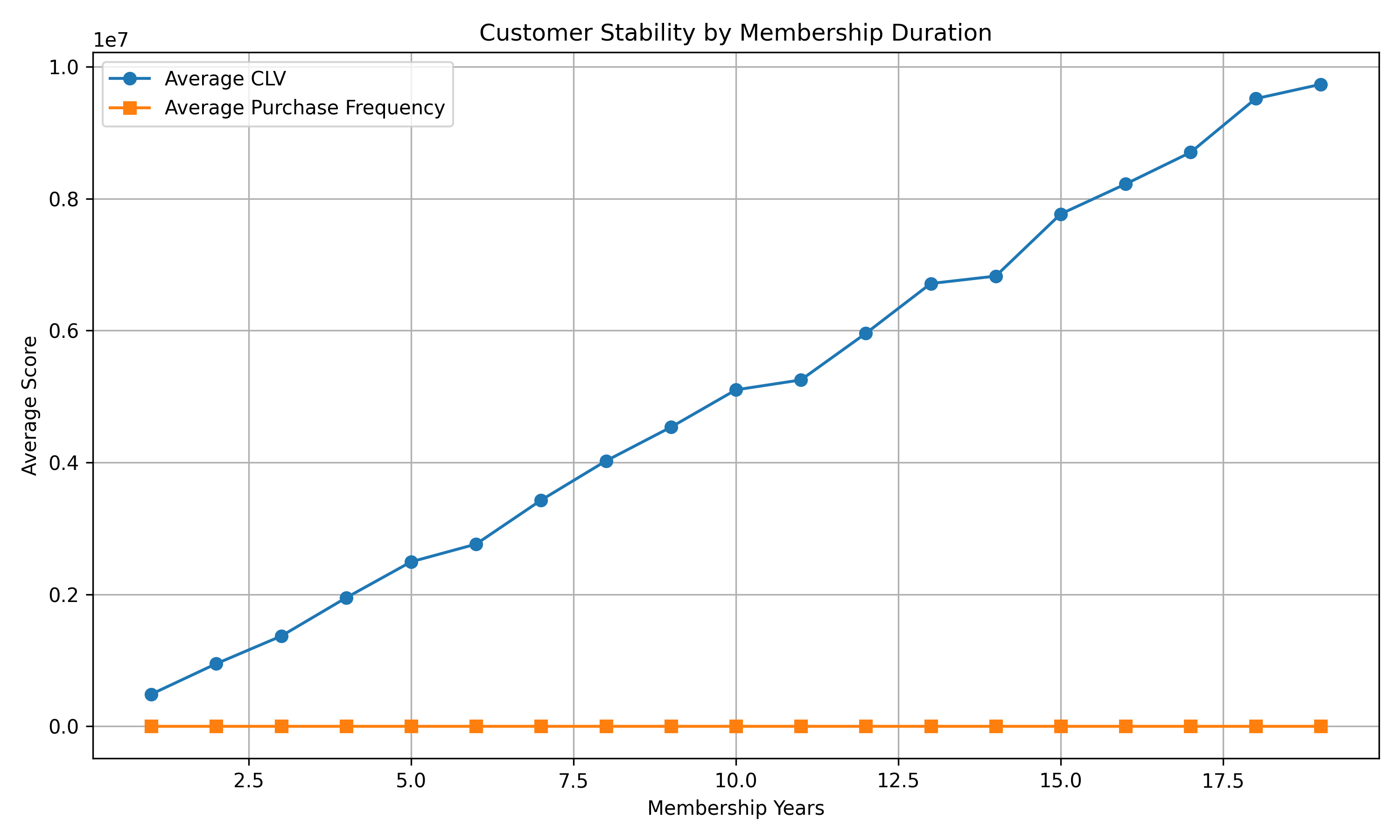
Goals Alignment:
The business goals are to:
- Enhance customer engagement through personalized marketing and loyalty programs.
- Reduce churn by identifying low-engagement or low-value segments and targeting them with retention strategies.
- Maximize revenue by identifying high-value customers and focusing efforts on these groups.
These findings align directly with the company's strategic priorities:
- Targeted Marketing: By identifying 3 distinct customer segments, marketing efforts can be more personalized and effective, ensuring campaigns are tailored to the needs of each segment.
- Retention and Upselling: Focusing on Cluster 2 (Loyal High Spenders) for upselling and loyalty programs and addressing the risk of churn in Cluster 1 aligns with the goal of maximizing revenue and customer retention.
- Resource Allocation: The segmentation allows for optimized resource allocation by focusing efforts on high-value, high-potential customers while addressing the needs of low-value or inactive segments.
Impact:
- Revenue Growth: By targeting Cluster 2 with loyalty programs and personalized upsell offers, the business can increase overall revenue.
- Churn Prevention: Identifying Cluster 1 as at-risk customers enables the company to take proactive measures, reducing churn and increasing customer lifetime value.
- Operational Efficiency: Segmenting customers based on behavior and engagement allows for more effective resource allocation, ensuring that marketing efforts, inventory, and product offerings align with customer needs.
Data Interpretation:
- Cluster 2 (Loyal High Spenders): Exhibits strong potential for increasing value through personalized engagement. Their high engagement, spending, and frequency make them ideal targets for targeted promotions, loyalty programs, and cross-selling initiatives.
- Cluster 1 (Low-Value Inactives): Demonstrates low engagement and spending, indicating they may be at risk of churn. Their lower-than-expected activity, combined with their long tenure, suggests that while they were once valuable, their behavior is now stagnating. Reactivating these customers with tailored promotions or loyalty incentives could help increase their engagement.
- Cluster 0 (Silent High-Value): Represents customers who have a high CLV but engage infrequently. These customers may have made a large initial purchase but haven't interacted much since. These customers can be targeted for special offers or re-engagement strategies to boost their activity without over-relying on frequent transactions.
Contextual Factors:
- Market Trends: Shifts in consumer behavior, such as a growing preference for digital engagement or changes in purchasing power, may influence how customers in each segment behave over time. Understanding these trends can help refine marketing strategies.
- Economic Factors: Broader economic conditions, such as disposable income levels, could affect customer spending behavior, especially in lower-value segments where spending sensitivity is higher.
Recommendation:
The analysis provides a roadmap for tailoring marketing efforts, engagement strategies, and retention plans. By focusing on high-value customers in Cluster 2 and addressing the risk of churn in Cluster 1, the business can improve customer retention and increase revenue. Additionally, targeting Cluster 0 with re-engagement offers can help capitalize on their high potential without expecting consistent frequent engagement.
- Focus on High-Potential Segments: Develop targeted loyalty programs, special offers, and upselling campaigns for Cluster 2 (Loyal High Spenders). These customers have high engagement and are likely to respond well to personalized promotions.
- Reactivation Campaigns for At-Risk Customers: For Cluster 1 (Low-Value Inactives), launch reactivation campaigns focused on re-engaging these customers. Consider offering incentives or tailored promotions to bring them back into the fold, as they show moderate engagement and tenure but need renewed attention.
- Re-engagement Strategies for Silent High-Value Customers: For Cluster 0 (Silent High-Value) customers, implement targeted re-engagement efforts, such as exclusive offers or high-value product recommendations, to bring them back into regular purchasing activity.
- Long-Term Retention Strategies: Invest in long-term retention strategies, as the data suggests that CLV increases with tenure. Focus on retaining customers from Cluster 2 while increasing engagement for other segments.
Conclusion:
The analysis provides valuable insights into customer behavior and highlights actionable opportunities to increase customer retention and maximize revenue. By leveraging segmentation insights, the business can implement personalized marketing campaigns, re-engagement strategies, and loyalty programs tailored to the needs of each segment. These data-driven decisions will help the company achieve its strategic goals of growth, customer retention, and optimized resource allocation.